Programming Java
Tasks studies - laboratory
Project maintained by dawidolko Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by dawidolko
OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
GUI JAVA SWING LABORATORIUM
JTREE, JTABBEDPANE, JSPLITPANE, JEDITORPANE, JSCROLLBAR
JTREE
public class JTree extends JComponent implements Scrollable, Accessible
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JTree() |
Creates a JTree with a sample model. |
JTree(Object[] value) |
Creates a JTree with every element of the specified array as the child of a new root node. |
JTree(TreeNode root) |
Creates a JTree with the specified TreeNode as its root, which displays the root node. |
ĆWICZENIE 1. Zaimplantuj aplikacje zgodnie z poniższym widokiem.
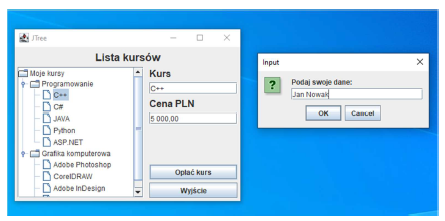
Po wybraniu odpowiedniego kursu wyświetli się informacje o nazwie i cenie. Kliknięcie Opłać kurs powoduje pojawienie się okienka do wpisania danych, wyjście zamyka okno.
JTABBEDPANE
public class JTabbedPane extends JComponent implements Serializable, Accessible, SwingConstants
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JTabbedPane() |
Creates an empty TabbedPane with a default tab placement of JTabbedPane.Top. |
JTabbedPane(int tabPlacement) |
Creates an empty TabbedPane with a specified tab placement. |
JTabbedPane(int tabPlacement, int tabLayoutPolicy) |
Creates an empty TabbedPane with a specified tab placement and tab layout policy. |
JSPLITPANE
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JSplitPane() |
It creates a new JSplitPane configured to arrange the child components side-by-side horizontally, using two buttons for the components. |
JSplitPane(int newOrientation) |
It creates a new JSplitPane configured with the specified orientation. |
JSplitPane(int newOrientation, boolean newContinuousLayout) |
It creates a new JSplitPane with the specified orientation and redrawing style. |
JSplitPane(int newOrientation, boolean newContinuousLayout, Component newLeftComponent, Component newRightComponent) |
It creates a new JSplitPane with the specified orientation and redrawing style, and with the specified components. |
JSplitPane(int newOrientation, Component newLeftComponent, Component newRightComponent) |
It creates a new JSplitPane with the specified orientation and the specified components. |
JEDITORPANE
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JEditorPane() |
It creates a new JEditorPane. |
JEditorPane(String url) |
It creates a JEditorPane based on a string containing a URL specification. |
JEditorPane(String type, String text) |
It creates a JEditorPane that has been initialized to the given text. |
JEditorPane(URL initialPage) |
It creates a JEditorPane based on a specified URL for input. |
JSCROLLBAR
public class JScrollBar extends JComponent implements Adjustable, Accessible
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JScrollBar() |
Creates a vertical scrollbar with the initial values. |
JScrollBar(int orientation) |
Creates a scrollbar with the specified orientation and the initial values. |
JScrollBar(int orientation, int value, int extent, int min, int max) |
Creates a scrollbar with the specified orientation, value, extent, minimum, and maximum. |
PRZYKŁAD 1
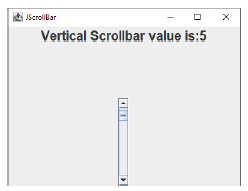
package LAB04;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent;
import java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener;
public class JScrollBar extends JFrame{
private javax.swing.JPanel JPanel;
private javax.swing.JScrollBar scrollBar1;
private JLabel label;
public static void main(String[] args) {
JScrollBar example = new JScrollBar();
example.setVisible(true);
}
public JScrollBar() {
super("JScrollBar");
this.setContentPane(this.JPanel);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
this.setSize(400, 300);
scrollBar1.addAdjustmentListener(new AdjustmentListener() {
@Override
public void adjustmentValueChanged(AdjustmentEvent e) {
label.setText("Vertical Scrollbar value is:"+
scrollBar1.getValue());
}
});
}
}
Tasks to solve on your own
Task 1.
Create an application window containing basic GUI components in the layout shown in the diagram below:
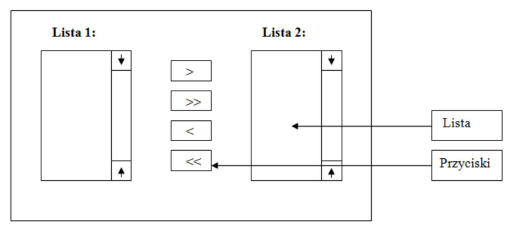
Add the following event handler to the interface designed in this way:
Pressing one of the four buttons should generate the following actions:
• for the “>” button – the selected item is transferred from List 1 to List 2
• for the “»” button – all items are transferred from List 1 to List 2
• for the “<” button – the selected item is transferred from List 2 to List 1
• for the “«” button – all items are transferred from List 2 to List 1
Task 2.
Create an editor application window containing basic GUI components in the layout shown in the diagram provided.
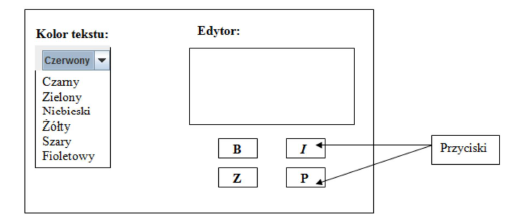
Add the following event handler to the designed interface:
• selecting one of the six available colors from the drop-down list should allow you to modify the color of the editor text field
• the default color for the editor is gray, while for text - black
• pressing one of the four buttons should generate the following actions:
o for button B - the text in the editor is bolded
o for button I - the text in the editor is tilted
o for button Z - the font size is decreased by -1 each time this button is pressed
o for button P - the font size is increased by +1 each time this button is pressed