Programming Java
Tasks studies - laboratory
Project maintained by dawidolko Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by dawidolko
OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
GUI JAVA SWING LABORATORIUM
JCHACKBOX, JPASSWORDFIELD, JRADIOBUTTON, JTEXTAREA
JTEXTAREA
public class JTextArea extends JTextComponent
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JTextArea() |
Creates a text area that displays no text initially. |
JTextArea(String s) |
Creates a text area that displays specified text initially. |
JTextArea(int row, int column) |
Creates a text area with the specified number of rows and columns that displays no text initially. |
JTextArea(String s, int row, int column) |
Creates a text area with the specified number of rows and columns that displays specified text. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
void setRows(int rows) |
It is used to set specified number of rows. |
void setColumns(int cols) |
It is used to set specified number of columns. |
void setFont(Font f) |
It is used to set the specified font. |
void insert(String s, int position) |
It is used to insert the specified text on the specified position. |
void append(String s) |
It is used to append the given text to the end of the document. |
EXAMPLE 1– SOURCE CODE AVAILABLE IN PROVIDED MATERIALS.
package JTextArea;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class TextAreaExample extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
// JFrame
static JFrame f;
// JButton
static JButton b, b1, b2, b3;
// label to display text
static JLabel l, l1;
// textarea
static JTextArea jt;
// default constructor
TextAreaExample(){ }
//mainclass
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create a new frame to store text field and button
f = new JFrame("textfield");
// create a label to display text
l = new JLabel("nothing entered");
l1 = new JLabel("0 lines");
// create a new buttons
b = new JButton("submit");
b1 = new JButton("plain");
b2 = new JButton("italic");
b3 = new JButton("bold");
// create an object of the text class
TextAreaExample te = new TextAreaExample();
// addActionListener to button
b.addActionListener(te);
b1.addActionListener(te);
b2.addActionListener(te);
b3.addActionListener(te);
// create a text area, specifying the rows and columns
jt = new JTextArea("please write something", 10, 10);
JPanel p = new JPanel();
// add the text area and button to panel
p.add(jt);
p.add(b);
p.add(b1);
p.add(b2);
p.add(b3);
p.add(l);
p.add(l1);
f.add(p);
// set the size of frame
f.setSize(300, 300);
f.show();
}
// if the button is pressed
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
String s = e.getActionCommand();
if (s.equals("submit")) {
// set the text of the label to the text of the field
l.setText(jt.getText() + ", ");
l1.setText(jt.getLineCount() + " lines");
}
else if (s.equals("bold")) {
// set bold font
Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 15);
jt.setFont(f);
}
else if (s.equals("italic")) {
// set italic font
Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.ITALIC, 15);
jt.setFont(f);
}
else if (s.equals("plain")) {
// set plain font
Font f = new Font("Serif", Font.PLAIN, 15);
jt.setFont(f);
}
}
}
JPASSWORDFIELD
public class JPasswordField extends JTextField
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JPasswordField() |
Constructs a new JPasswordField, with a default document, null starting text string, and 0 column width. |
JPasswordField(int columns) |
Constructs a new empty JPasswordField with the specified number of columns. |
JPasswordField(String text) |
Constructs a new JPasswordField initialized with the specified text. |
JPasswordField(String text, int columns) |
Construct a new JPasswordField initialized with the specified text and columns. |
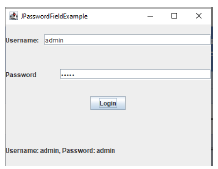
Exercise 1.
You should propose a GUI shown in the figure below, which has the following functionalities:
after entering the username and password and clicking on login, the entered data should appear in the label tab.
JRADIOBUTTON
public class JRadioButton extends JToggleButton implements Accessible
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JRadioButton() |
Creates an unselected radio button with no text. |
JRadioButton(String s) |
Creates an unselected radio button with specified text. |
JRadioButton(String s, boolean selected) |
Creates a radio button with the specified text and selected status. |
Commonly usedMethods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
void setText(String s) |
It is used to set specified text on button. |
String getText() |
It is used to return the text of the button. |
void setEnabled(boolean b) |
It is used to enable or disable the button. |
void setIcon(Icon b) |
It is used to set the specified icon on the button. |
Icon getIcon() |
It is used to get the icon of the button. |
void setMnemonic(int a) |
It is used to set the mnemonic on the button. |
void addActionListener(ActionListener a) |
It is used to add the action listener to this object. |
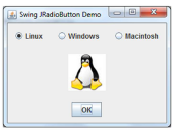
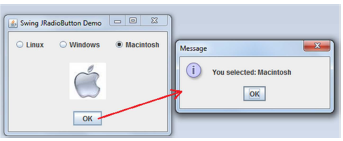
Exercise 2.
Design the GUI as shown in the figure below, and then implement appropriate program operation, which after selecting the system will display the system icon, and pressing the OK button will display the selected system message.
## JCHACKBOX
public class JCheckBox extends JToggleButton implements Accessible
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
JCheckBox() |
Creates an initially unselected check box button with no text, no icon. |
JCheckBox(String s) |
Creates an initially unselected check box with text. |
JCheckBox(String text, boolean selected) |
Creates a check box with text and specifies whether or not it is initially selected. |
JCheckBox(Action a) |
Creates a check box where properties are taken from the Action supplied. |
Commonly usedMethods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
AccessibleContext getAccessibleContext() |
It is used to get the AccessibleContext associated with this JCheckBox. |
protected String paramString() |
It returns a string representation of this JCheckBox. |
Example GUI with chackBox elements
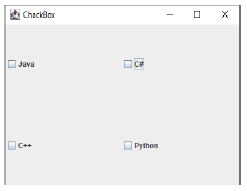
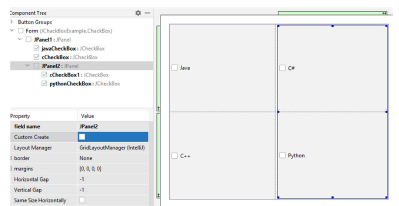
Exercise 3.
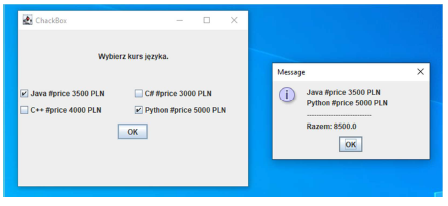
Design the application according to the drawing below. After selecting the appropriate course and clicking the Ok button, the user will receive a message with information about the final price for the selected courses .
Tasks to solve yourself
Task 1.
A GUI application should be proposed, the example of which is presented below, the application should have the following functionalities:
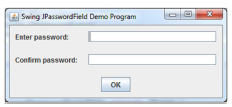
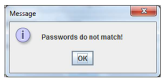
• After entering the password and clicking OK the application checks the correctness of passwords, in case of different passwords the message “Passwords are not matched!” should appear
• If the passwords match but are not equal (“codejava”), the following message will appear:
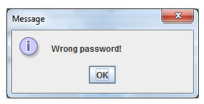
• If both passwords are equal (“codejava”) the following message should appear:
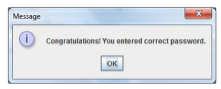
Task 2.
Using the components you have learned, you should design an application that will demonstrate the use of available methods for the components discussed.