Programming Java
Tasks studies - laboratory
Project maintained by dawidolko Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by dawidolko
OBJECT-ORIENTED PROGRAMMING JAVA – LABORATORY
CLASSES
CLASS DEFINITION
public class ClassName {
// Field definitions
// Constructor definitions
// Method definitions
}
public class Person {
// Field definitions
String firstName = "John", lastName = "Doe";
int age = 11;
// Constructor definitions
// Method definitions
public void info() {
System.out.println("First Name Last Name: " + firstName + " " + lastName + "\nAge: " + age);
}
}
CREATING CLASS OBJECTS
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of the Person class
Person person1 = new Person();
// Calling the method
person1.info();
}
}
GETTER AND SETTER METHODS
public class Person {
// Field definitions
String firstName = "John", lastName = "Doe";
int age = 11;
// Constructor definitions
// Method definitions
public void info() {
System.out.println("First Name Last Name: " + firstName + " " + lastName + "\nAge: " + age);
}
// Getter and setter methods
// Getters and setters are methods that allow accessing
// or modifying private fields of the class from the outside.
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person obj = new Person();
obj.setFirstName("John");
obj.setLastName("Doe");
obj.setAge(11);
obj.info();
}
}
CONSTRUCTOR
The constructor’s task is to initialize an object during its creation. A constructor has the same name as the class and, syntactically, is similar to a method. However, constructors do not have a return type. Typically, a constructor assigns initial values to the object’s member variables or performs other operations required to set up the object.
public class Person {
// Field definitions
String firstName = "John", lastName = "Doe";
int age = 11;
// Constructor definitions
// No-argument constructor
public Person() {
// Constructor body
}
// Constructor with arguments
public Person(String firstName, String lastName, int age) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.age = age;
}
// Method definitions
public void info() {
System.out.println("First Name Last Name: " + firstName + " " + lastName + "\nAge: " + age);
}
}
public class Calculator {
double a, b;
public double sum(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}
JAVA STRING
public class JavaStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "Java", str2 = "Java", str3 = "C#";
String str4 = "Object-Oriented Programming - ";
System.out.println(str1);
System.out.println(str3);
// String class methods
// length()
System.out.println("Length of text: " + str1.length());
// concat() - concatenating two Strings
// str1.concat(str2);
System.out.println(str4.concat(str1));
// equals() - method to compare strings
boolean result1 = str1.equals(str2);
System.out.println("Comparison of str1 and str2: " + result1);
boolean result2 = str1.equals(str3);
System.out.println("Comparison of str1 and str3: " + result2);
}
}
Escape Character in Java String
In Java, strings are stored within quotation marks. Thus, the code String example = "This is the "String" class"; will result in an error. However, using the escape character \ allows the following definition:
String example = "This is the \"String\" class";
The escape character makes the compiler read the above text as a single string.
Creating Strings Using the new Operator
public class JavaStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringNew();
}
public static void StringNew() {
String str1 = new String("Sample text");
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
SELECTED STRING CLASS METHODS
Method Description
contains() checks whether the string contains a substring
substring() returns the substring of the string
join() joins the given strings using the delimiter
replace() replaces the specified old character with the specified new character
replaceAll() replaces all substrings matching the regex pattern
replaceFirst() replaces the first matching substring
charAt() returns the character present in the specified location
getBytes() converts the string to an array of bytes
indexOf() returns the position of the specified character in the string
compareTo() compares two strings in dictionary order
compareToIgnoreCase() compares two strings ignoring case differences
trim() removes any leading and trailing whitespaces
format() returns a formatted string
split() breaks the string into an array of strings
toLowerCase() converts the string to lowercase
toUpperCase() converts the string to uppercase
valueOf() returns the string representation of the specified argument
toCharArray() converts the string to a char array
matches() checks whether the string matches the given regex
startsWith() checks if the string begins with the given string
endsWith() checks if the string ends with the given string
isEmpty() checks whether a string is empty
intern() returns the canonical representation of the string
contentEquals() checks whether the string is equal to CharSequence
hashCode() returns a hash code for the string
subSequence() returns a subsequence from the string
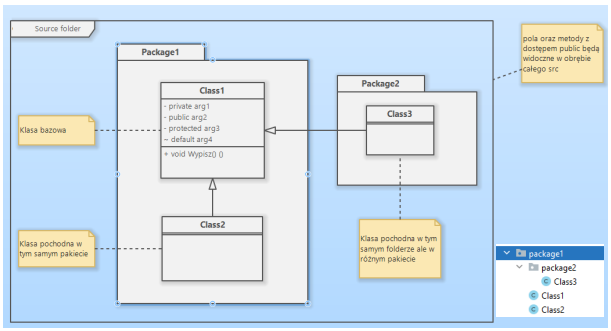
ACCESS MODIFIERS
-
default – declarations visible within the package (package-private)
-
private – access within the class only
-
protected – access within the package and in derived classes
-
public – access across the entire project
this OPERATOR
The keyword this is used to refer to the current object within a method or constructor.
package PO_UR;
public class Person {
String firstName = "John", lastName = "Doe";
int age = 11;
Person(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
System.out.println("this reference " + this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person obj1 = new Person("John");
System.out.println("object reference: " + obj1);
}
}
Output:
this reference PO_UR.Person@119d7047
object reference: PO_UR.Person@119d7047
The reference to both the object and this is the same.
PASSING AN OBJECT AS A METHOD ARGUMENT
public class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
System.out.println("Initial values x = " + this.x + ", y = " + this.y);
// Calling the add method
add(this);
System.out.println("Values of x and y after passing the object to the method x = " + this.x + ", y = " + this.y);
}
void add(Point point) {
point.x += 2;
point.y += 2;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point obj1 = new Point(1, -2);
}
}
JAVA INSTANCEOF OPERATOR
Operator wykorzystywany do sprawdzania czy obiekt jest instancją klasy.
public class ExampleInstanceof {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Programiz";
// checks if name is instance of String
boolean result1 = name instanceof String;
System.out.println("name is an instance of String: " + result1);
// create an object of class
ExampleInstanceof obj = new ExampleInstanceof();
// checks if obj is an instance of Main
boolean result2 = obj instanceof ExampleInstanceof;
System.out.println("obj is an instance of Main: " + result2);
}
}
JAVA INSTANCEOF OPERATOR
Operator used to check whether an object is an instance of a class.
public class ExampleInstanceof {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Programiz";
// checks if name is instance of String
boolean result1 = name instanceof String;
System.out.println("name is an instance of String: " + result1);
// create an object of class
ExampleInstanceof obj = new ExampleInstanceof();
// checks if obj is an instance of Main
boolean result2 = obj instanceof ExampleInstanceof;
System.out.println("obj is an instance of Main: " + result2);
}
}
Tasks to solve on your own:
Task 1.
In the new package, create classes describing the following geometric figures: Circle, Square,
Rectangle, Cube, Cuboid, Sphere, Cone. For each class, select the appropriate fields.
Also create methods to calculate the areas of figures, perimeters (for flat figures), and volumes (for spatial figures). For each class, create a method that displays data about the figure, i.e. name, parameters, value of area and perimeter or volume. Create objects of these figures and show the results of the calculations using the data display function. Create a calculator for geometric figures, i.e. the appropriate menu allowing: selecting a geometric figure and entering parameters for this figure from the console. Then display the results using the method that displays data.
Task 2.
Create a class that stores information about the Building (name, year of construction, number of floors). Prepare
a method that displays all information about the building, and a method that calculates how old the building is
(you can set the current year to a fixed value). Create several objects (buildings), set their values and
call methods for them. The LocalData class should be used to calculate the date.### Task 3.
Create a program that will created several objects of the type Species. The Species class should contain the following fields: genus name, species name, chromosome number 2n,
basic chromosome number x, description and methods: giving the full name (Genus + species) ,
giving the haploid number of chromosomes n, printing all data, cloning the object –
the method should return a reference to a new object of type Species with the field values
the same as in the object in which it was called. All methods
```should be used in the program
```